
Because the carbon atom only has six valence electrons at this point, we must employ one lone pair from an oxygen to build a carbon–oxygen double bond. There are no remaining electrons for the centre atom.Ħ. We evenly distribute the remaining 18 electrons across the three oxygen atoms by attaching three lone pairs to each and showing the 2 charge:ĥ. Three bonding pairs between the oxygen and carbon atoms are formed using six electrons:Ĥ. This results in a total of 4 + (3*6) + 2 = 24 valence electrons.ģ.
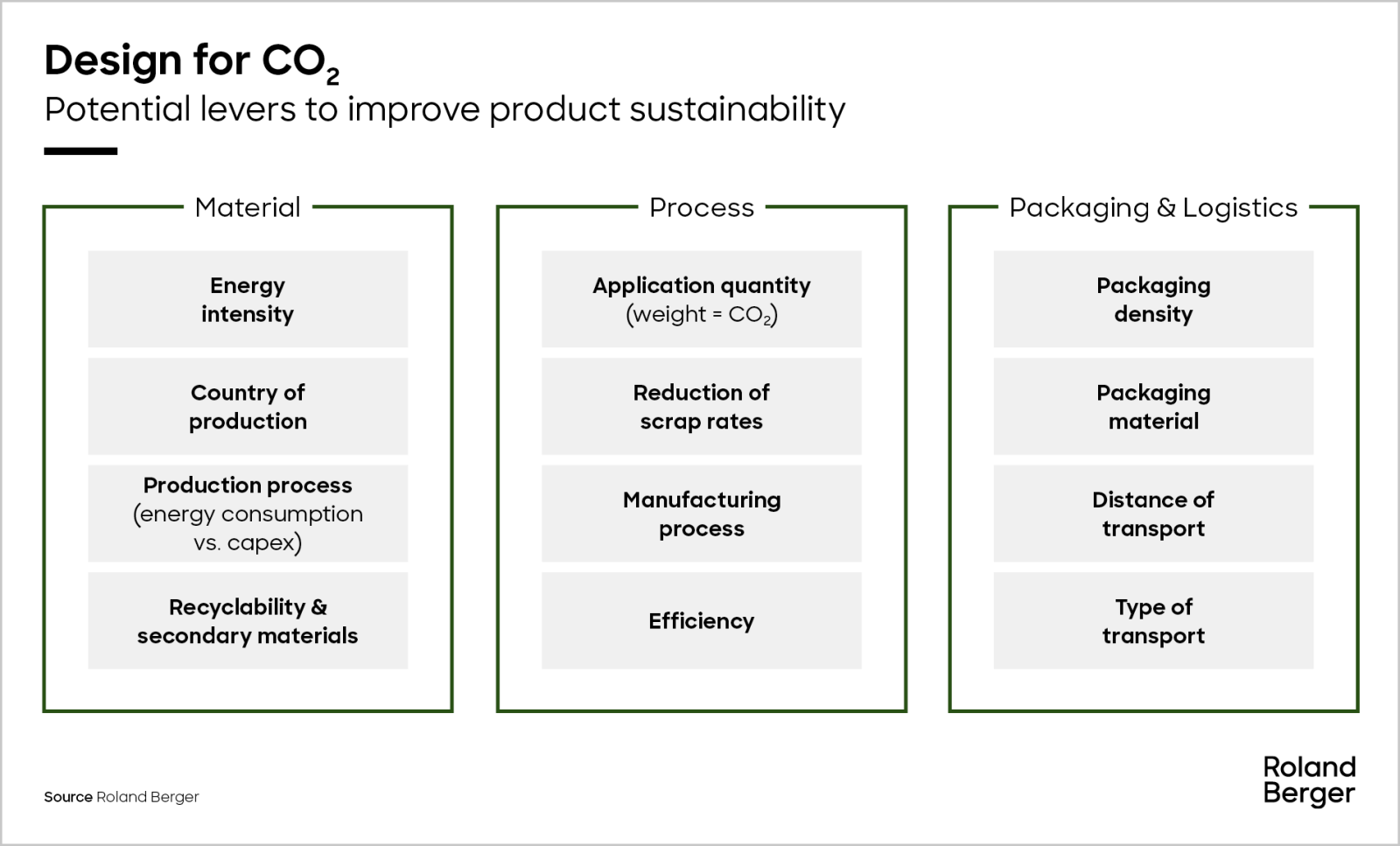
Carbon has four valence electrons, each oxygen has six, and there are two more for the valence charge of two. Due to the fact that carbon is the least electronegative element, it is positioned centrally:Ģ. Unlike O 3, however, CO 3 2- ‘s real structure is a composite of three resonance structures.ġ.
#CHARGE OF CARBON IN CO3 HOW TO#
How to draw resonance structure of carbonate ionĪs with ozone, the carbonate ion’s electronic structure cannot be explained by a single Lewis electron structure. A dashed line indicates the solitary link between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The carbon atom is connected to a single oxygen atom and a chlorine atom in the fourth resonance structure. The carbon atom is connected to a single oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom in the third resonance structure. The carbon atom is connected to a single oxygen atom and a second carbon atom in the second resonance structure. A dashed line indicates the double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The carbon atom is connected to two oxygen atoms in the first resonance structure.
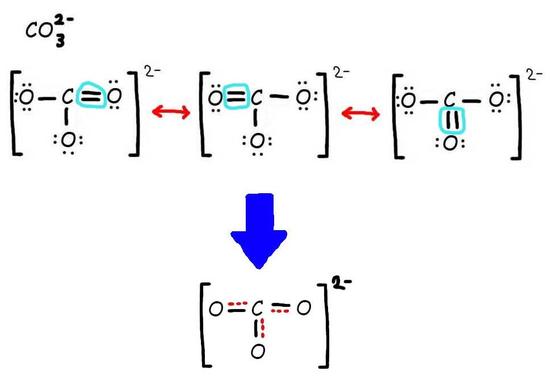
Numerous contributing structures are used to depict a molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons (also called resonance structures or canonical forms). Resonance is a term used to describe delocalized electrons within specific compounds or polyatomic ions whose bonding cannot be represented using a single Lewis formula. The electrons in a resonance structure participate in more than one covalent bond, and the electron pairs are shared between the atoms in diverse ways.Įven when formal charges are taken into account, the bonding of certain molecules or ions cannot always be described by a single Lewis structure. The resonance structures are drawn with the same link lengths and angles, and the electrons are dispersed in the same way between the atoms. The different structures are called resonance structures because they “resonate” with each other, implying that they are all equally acceptable representations of the molecule. Resonance structures are capable of explaining delocalized electrons that cannot be described in an integer number of covalent bonds using a single Lewis formula. The term “resonance structure” refers to a collection of two or more Lewis Structures that together describe the electronic bonding of a single polyatomic species, including fractional bonds and charges.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
